| . |  |
. |
Paris (AFP) July 14, 2010 Two millennia of foreign invasions and internal wars in China were driven more by cooling climate than by feudalism, class struggle or bad government, a bold study released Wednesday argued. Food shortages severe enough to spark civil turmoil or force hordes of starving nomads to swoop down from the Mongolian steppes were consistently linked to long periods of colder weather, the study found. In contrast, the Central Kingdom's periods of stability and prosperity occurred during sustained warm spells, the researchers said. Theories that weather-related calamities such as drought, floods and locust plagues steered the unraveling or creation of Chinese dynasties are not new. But until now, no one had systematically scanned the long sweep of China's tumultuous history to see exactly how climate and Chinese society might be intertwined. Chinese and European scientists led by Zhibin Zhang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing decided to compare two sets of data over 1,900 years. Digging into historical archives, they looked at the frequency of war, price hikes of rice, locust plagues, droughts and floods. For conflict, they distinguished between internal strife and external wars. At the same time, they reconstructed climate patterns over the period under review. "The collapses of the agricultural dynasties of the Han (25-220), Tang (618-907), Northern Song (960-1125), Southern Song (1127-1279) and Ming (1368-1644) are closely associated with low temperature or the rapid decline in temperature," they conclude. A shortage of food would have weakened these dynasties, and pushed nomads in the north -- even more vulnerable to dips in temperature -- to invade their southern, Chinese-speaking neighbours, the authors argued. A drop of 2.0 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) in average annual air temperature can shorten the growing season for steppe grasses, which are critical for livestock, by up to 40 days. "When the climate worsens beyond what the available technology and economic system can compensate for, people are forced to move or starve," they said. The study found more droughts and floods during cold periods, but the factors that contributed most directly to wars and dynastic breakup were soaring rice prices and locust infestations. The Roman and Mayan empires, they noted, also fell during cold periods. Zhang and colleagues speculated that periodic temperature shifts roughly every 160 or 320 years were related to natural climate changes, namely fluctuations in solar activity and in Earth's orbit and axial spin. The team said the findings demonstrate that climate change can lead to unrest and warfare. "Historians commonly attribute dynastic transitions or cycles to the quality of government and class struggles," according to the paper, published in the British journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B. "However, climatic fluctuation may be a significant factor interacting with social structures in affecting the rise and fall of cultures and dynasties." But the historical evidence they found points to global cooling, not to global warming, as the culprit. The scientists were cautious about making projections for the future. In 2007, the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said that man-made warming this century will lead to worse droughts, floods, harsh storms and sea level rise, with the potential to inflict hunger and misery on millions.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Climate Science News - Modeling, Mitigation Adaptation
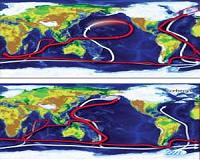 Global Backup Generator For Past Climate Change
Global Backup Generator For Past Climate ChangeHonolulu HI (SPX) Jul 13, 2010 Toward the end of the last ice age, a major reorganization took place in the current system of the North Pacific with far-reaching implications for climate, according to a new study published in the July 9, 2010, issue of Science by an international team of scientists from Japan, Hawaii, and Belgium. Earth's climate is regulated largely by the world ocean's density-driven circulation, whic ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |