| . |  |
. |
Basque, Spain (SPX) Apr 25, 2011 Neiker-Tecnalia (the Basque Institute for Agricultural Research and Development) is working on the development of new biotechnological tools to produce in vitro selected trees of the Pinus genus. Scientists at this technological centre have developed various techniques for propagation of Pinus radiata, Pinus pinea, Pinus pinaster and Pinus sylvestris by using tissue culture. These methodologies enable obtaining a great quantity of clonal material, which can be used both in genetic improve programmes and experimentation, and in programmes of reforestation according to market demands. The research was carried out by the Tissue Culture team led by Paloma Moncalean, within the remit of the Neiker-Tecnalia Genetic Improve programme. The main aim was the development and optimisation of biotechnological tools for obtaining Pinus radiata D. Don clonal material (also known as Monterey pine) from somatic embryogenesis. This technique involves the development of embryos from non-sexual cells. On being stimulated, these stop expressing the genes doing so up to then, and the cells start to behave as if they were sexual and give rise to new, genetically identical individuals (clones). The research is part of Ms Itziar Montalban's PhD, involving the optimisation of all phases of the embryogenic process, enabling obtaining 1,600 seedlings per gram of embryogenic tissue, a figure which represents the best results described to date with the Pinus genus.
Programmes of clonal forestry All these techniques have a direct relation with economic profitability and with sustainable forestry management, as they enable obtaining enhanced quality plants and reproducing or conserving threatened individuals and species, through the conservation of their germoplasm for the future.
Biotechnology in the forestry sector When these go from the young stage to the adult one, a series of physiological and morphological changes are produced, which causes a deep loss of their regeneration potential by traditional asexual means. This is why experts combine traditional propagation techniques (grafting, root stocks, etc.) with new biotechnological tools such as in vitro cultures. For decades now, a number of multinational firms such as ArborGen, Genfor, Mininco, and Weyerhaeuser and Spanish companies such as Agromillora Catalana, Cultesa and Vitrotech Biotecnologia Vegetal have applied and developed biotechnological tools for obtaining the selected cloned material required by the market. Various international companies are developing biotechnological tools for obtaining the selected cloned material, which is why Neiker-Tecnalia started to work on the development of selected plant tissue culture techniques a number of years ago, given their quantitative and qualitative value. Currently, Neiker-Tecnalia is working closely with Invitrotek, a Basque company specialising in the in vitro production of high value-added plants.
Forest mass in Spain Pine trees are represented in Spain by seven autochthonous species. Of these, only the Pinus radiata achieves notable territorial significance, with six million hectares, and a figure which is set to increase given that one of the objectives of the Spanish Forestry Plan is the plantation of 1,000 million new trees over the next decade.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Basque Institute for Agricultural Research and Development Forestry News - Global and Local News, Science and Application
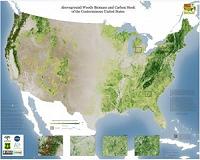 WHRC debuts detailed maps of forest canopy height and carbon stock for the conterminous US
WHRC debuts detailed maps of forest canopy height and carbon stock for the conterminous USFalmouth, MA (SPX) Apr 25, 2011 The Woods Hole Research Center has released the first hectare-scale maps of canopy height, aboveground biomass, and associated carbon stock for the forests and woodlands of the conterminous United States. The multi-year project, referred to as the National Biomass and Carbon Dataset (NBCD), produced maps of these key forest attributes at an unprecedented spatial resolution of 30 m. Accordi ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |