| . |  |
. |
Canberra, Australia (SPX) Jan 02, 2009 Long-term observations of the oceans around Australia are providing the nation's climate scientists with significant benchmarks for seasonal forecasts and monitoring future climate change. Initiated near the end of a two-year El Nino event in May 1983, the program involves the deployment of simple 'expendable instruments' (XBTs) from commercial shipping that measure temperature and currents to a depth of 800m along routes in the Indian, Pacific and Southern Oceans. "Today, we have over 60,000 measurements of temperature around Australia that scientists regularly use to assess past long-term trends - test models used to predict future climate or forecast ocean behaviour," says Dr Meyers, who leads Australia's Integrated Marine Observing System (IMOS). "There is so much ocean around Australia influencing our daily weather and longer term climate that it made sense to begin a record from which we could connect ocean change to shifts in rainfall patterns across southern Australia," says Dr Gary Meyers who, with colleagues at CSIRO, the Bureau of Meteorology (BoM) and the Scripps Institute of Oceanography in the US, established the ocean monitoring system. "The 1982/83 El Nino came as a big surprise when we saw all kinds of changes around Australia but didn't understand them. Now these ocean temperature data contribute to the BoM's routine seasonal climate forecast." At 25 years the system stands as one of the longest sustained ocean observing networks in the world, and is a rare long-term record of ocean change in the huge and poorly monitored Southern Hemisphere ocean domain. Based on the records, CSIRO's Dr Susan Wijffels and co-authors will publish a landmark paper on the mean currents flowing between Australia and Indonesia in the Journal of Physical Oceanography. These currents form a critical ocean interconnection - the so-called Indonesian Throughflow - in the distribution of heat in the global climate system. "Today, we have over 60,000 measurements of temperature around Australia that scientists regularly use to assess past long-term trends - test models used to predict future climate or forecast ocean behaviour," says Dr Meyers, who leads Australia's Integrated Marine Observing System (IMOS). "More than 50 scientific publications and books have been published using the Australian data." Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research (CAWCR) Water News - Science, Technology and Politics
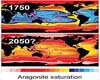 Sydney (AFP) Jan 2, 2009
Sydney (AFP) Jan 2, 2009A sharp slowdown in coral growth on Australia's Great Barrier Reef since 1990 is a warning sign that precipitous changes in the world's oceans may be imminent, scientists said Friday. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |