| . |  |
. |
Boulder CO (SPX) May 23, 2011 Cigarette smoking, forest fires and woodburning can release a chemical that may be at least partly responsible for human health problems related to smoke exposure, according to a new study by NOAA researchers and their colleagues. Using a custom mass spectrometer designed by the researchers, the NOAA-led team was able get the first look at levels of the chemical, isocyanic acid, in the atmosphere. Isocyanic acid has been difficult to detect with conventional measurement techniques. "We found isocyanic acid in a number of places, from air in downtown Los Angeles and air downwind of a Colorado wildfire, to cigarette smoke," said Jim Roberts, lead author of the new paper and a chemist with NOAA's Earth System Research Laboratory in Boulder, Colo. "We also demonstrated that it dissolves readily in water, which means that humans can be exposed directly if it gets into eyes or lungs." The health effects of such exposure are not fully known. In the body isocyanic acid, described by the chemical formula HNCO, is part of a biochemical pathway linked with cataracts and inflammation that can trigger cardiovascular disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Until now, the acid had not been measured in air outdoors or in tobacco smoke.
The research team made four separate measurements of HNCO: + in the air in Boulder downwind of the fall 2010 Fourmile Canyon wildfire; + in laboratory burning experiments at high concentrations; + and in cigarette smoke. The team also made the first measurements of the acid's ability to dissolve in water, which determines the chemical's tendency to dissolve into moist tissues in the body. "There are literally billions of people in the world who burn biomass for cooking and heating," Roberts said. "If these indoor fires release similar levels of isocyanic acid as the fires we studied in the laboratory, families could be exposed to high levels of the chemical." Roberts and colleagues from NOAA and University of Colorado at Boulder's Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, the, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University and the University of Montana published their paper in the May 17 edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The research project started in the Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory, where scientists burned brush, tree branches and other vegetation, to better understand the air quality effects of wildfires. They used a new, specialized instrument - a mass spectrometer built by Roberts and several colleagues - to measure the amounts of a suite of organic acids, which are emitted by burning vegetation. Such acids are involved in chemistry that can degrade air quality. During simulated wildfires in the Montana laboratory, levels of HNCO approached 600 parts per billion volume (ppbv). The HNCO was a few thousand times less concentrated in both the air in Los Angeles during a time without recent fires, and in the air in Boulder when the Fourmile Canyon fire was burning upwind. At about 1 ppbv, the research team calculated that enough HNCO would dissolve into exposed tissues - lungs and eyes - that those tissues could be vulnerable to "carbamylation," part of the chemical process triggering inflammation and cataract development. People could experience higher exposure to HNCO near wildfires or in indoor environments where coal, wood or other biomass is burned for heating or cooking. The health effects of chronic exposure to lower-level amounts isocyanic acid, such as those found in the California and Colorado air are not known. The extreme sensitivity of the new instrument to low concentrations of HNCO made it impossible to quantify the very high levels of isocyanic acid in cigarette smoke. "We conclude that tobacco-derived HNCO needs to be measured more extensively and potential exposure to it quantified," the scientists wrote, adding that the acid is not currently listed as a "harmful" or "potentially harmful" constituent in tobacco products or smoke. In their paper, researchers noted other sources of atmospheric HNCO, including pollution-control equipment that is being introduced in California and Europe to reduce emissions by diesel trucks. The systems are designed to reduce nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air quality problems, but they emit HNCO as a by-product. This new source could increase human exposure to the chemical in urban areas. Moreover, climate change is expected to bring hotter temperatures and drier conditions to some regions of the world, with accompanying increases in biomass burning, including wildfire. "We may be facing a future of higher amounts of HNCO in the atmosphere," said Roberts. "It is fortunate that now we can measure it." Other authors of the new paper, "Isocyanic acid in the atmosphere and its possible link to smoke related health effects," are Patrick R. Veres, Anthony K. Cochran, Carsten Warneke, Ian R. Burling, Robert J. Yokelson, Brian Lerner, Jessica B. Gilman, William C. Kuster, Ray Fall, and Joost de Gouw. Their information can be found here.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Custom Mass Spectrometer at NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory at NOAA Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) The Air We Breathe at TerraDaily.com
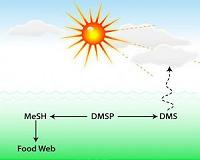 UGA scientists discover missing links in the biology of cloud formation over the oceans
UGA scientists discover missing links in the biology of cloud formation over the oceansAthens GA (SPX) May 13, 2011 Scientists have known for two decades that sulfur compounds that are produced by bacterioplankton as they consume decaying algae in the ocean cycle through two paths. In one, a sulfur compound dimethylsulfide, or DMS, goes into the atmosphere, where it leads to water droplet formation - the basis of clouds that cool the Earth. In the other, a sulfur compound goes into the ocean's food web, where ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |