| . |  |
. |
Dallas TX (SPX) Jan 21, 2009 The official State Dinosaur of Texas is up for a new name, based on Southern Methodist University research that proved the titleholder has been misidentified. State Rep. Charles Geren of Fort Worth filed a resolution Jan. 7 to change the name of the state dinosaur from Pleurocoelus to Paluxysaurus jonesi to correctly name the massive sauropod whose tracks and bones litter the central Texas Jones Ranch. Peter Rose is the scientist behind the name change: His master's level study of dinosaur bones at SMU eventually led him to dispute the long-accepted notion that the large, sauropod bones found in and around the Paluxy River near Glen Rose, Texas, were the same as Pleurocoelus bones first found in Maryland in the late 1800s. Rose determined it was a different dinosaur altogether - a previously unrecognized genus and species he named Paluxysaurus jonesi, after W.W. Jones, the owner of the land on which the fossils were found. Once Rose's discovery was published in 2007, Pleurocelus' grand Texas title no longer fit. Geren filed his resolution on behalf of constituents at the Fort Worth Museum of Science and History, which is a partner with SMU in ongoing research at the Glen Rose site, about 60 miles southwest of Fort Worth. Dr. Aaron Pan, Ph.D., the museum's curator of science, believes it's crucial to get the record corrected. "I think it's going to be good for Texas paleontology and dinosaur research in general," Pan said. "Peter Rose's research has found that it is a new genus and a new species. This dinosaur is unique to Texas, and it is the most abundant dinosaur fossil found in the Glen Rose area." SMU geological sciences professor Louis Jacobs, who was Rose's mentor, said that nobody before Rose had made an adequate study of the sauropod bones found at the Glen Rose site. Jacobs has described Texas as a kind of "free trade zone for the age of reptiles" since dinosaurs from three different geologic time periods have been found in three different geographic areas of the state. Paluxysaurus jonesi is believed to have lived 112 million years ago during the Cretaceous Period. "It just goes to show that Texas is a great place to make great discoveries - even when you might think everything has been found," Jacobs said. Rose, 29, received his master's degree in geological sciences from SMU in 2004. Currently pursuing a Ph.D. in paleontology at the University of Minnesota, he concedes he is excited about the proposal to change the state dinosaur's name to correspond with his research. "But when you come down to it, whether it's a new species is not the big question. More important are some of the bigger picture ideas about how these organisms evolved and what they were doing when they were alive. I hope the future work I do has some broader implications. Currently I'm doing more climate research with implications, I hope, for global climate change." Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Southern Methodist University Darwin Today At TerraDaily.com
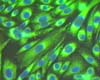 Nashville (UPI) Jan 20, 2009
Nashville (UPI) Jan 20, 2009 U.S. scientists say they have developed a technique that uses a scanning transmission electron microscope to "see" whole cells in liquid. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |