| . |  |
. |
Athens OH (SPX) Aug 21, 2008 A stalagmite in a West Virginia cave has yielded the most detailed geological record to date on climate cycles in eastern North America over the past 7,000 years. The new study confirms that during periods when Earth received less solar radiation, the Atlantic Ocean cooled, icebergs increased and precipitation fell, creating a series of century-long droughts. A research team led by Ohio University geologist Gregory Springer examined the trace metal strontium and carbon and oxygen isotopes in the stalagmite, which preserved climate conditions averaged over periods as brief as a few years. The scientists found evidence of at least seven major drought periods during the Holocene era, according to an article published online in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. "This really nails down the idea of solar influence on continental drought," said Springer, an assistant professor of geological sciences. Geologist Gerald Bond suggested that every 1,500 years, weak solar activity caused by fluctuations in the sun's magnetic fields cools the North Atlantic Ocean and creates more icebergs and ice rafting, or the movement of sediment to ocean floors. Other scientists have sought more evidence of these so-called "Bond events" and have studied their possible impact on droughts and precipitation. But studies to date have been hampered by incomplete, less detailed records, Springer said. The stalagmites from the Buckeye Creek Cave provide an excellent record of climate cycles, he said, because West Virginia is affected by the jet streams and moisture from the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Other studies have gleaned climate cycle data from lakes, but fish and other critters tend to churn the sediment, muddying the geological record there, said study co-author Harold Rowe, an assistant professor of geological sciences at the University of Texas at Arlington. "(The caves) haven't been disturbed by anything. We can see what happened on the scale of a few decades. In lakes of the Appalachian region, you're looking more at the scale of a millennium," Rowe said. Strontium occurs naturally in the soil, and rain washes the element through the limestone. During dry periods, it is concentrated in stalagmites, making them good markers of drought, Rowe explained. Carbon isotopes also record drought, Springer added, because drier soils slow biological activity. This causes the soil to "breathe less, changing the mix of light and heavy carbon atoms in it," he said. In the recent study, the scientists cut and polished the stalagmite, examined the growth layers and then used a drill to take 200 samples along the growth axis. They weighed and analyzed the metals and isotopes to determine their concentrations over time. The data are consistent with the Bond events, which showed the connection between weak solar activity and ice rafting, the researchers said. But the study also confirmed that this climate cycle triggers droughts, including some that were particularly pronounced during the mid-Holocene period, about 6,300 to 4,200 years ago. These droughts lasted for decades or even entire centuries. Though modern records show that a cooling North Atlantic Ocean actually increases moisture and precipitation, the historic climate events were different, Springer said. In the past, the tropical regions of the Atlantic Ocean also grew colder, creating a drier climate and prompting the series of droughts, he explained. The climate record suggests that North America could face a major drought event again in 500 to 1,000 years, though Springer said that manmade global warming could offset the cycle. "Global warming will leave things like this in the dust. The natural oscillations here are nothing like what we would expect to see with global warming," he said. Though some climate and drought records exist for the Western and Midwest areas of North America, the eastern Appalachian region hasn't been studied much to date, Rowe said. The research team plans to examine additional stalagmite records from West Virginia and Tennessee to paint a better picture of North American climate cycles. Collaborators on the study also included Lawrence Edwards, Ben Hardt and Hai Cheng of the University of Minnesota.
Community
Related Links Ohio University Climate Science News - Modeling, Mitigation Adaptation
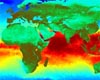 Huntsville AL (SPX) Aug 07, 2008
Huntsville AL (SPX) Aug 07, 2008A new study, co-funded by NASA, has identified a link between a warming Indian Ocean and less rainfall in eastern and southern Africa. Computer models and observations show a decline in rainfall, with implications for the region's food security. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |