| . |  |
. |
Ithaca NY (SPX) Nov 26, 2007 Using supercomputers to compare portions of the human genome with those of other mammals, researchers at Cornell have discovered some 300 previously unidentified human genes, and found extensions of several hundred genes already known. The discovery is based on the idea that as organisms evolve, sections of genetic code that do something useful for the organism change in different ways. The research is reported by Adam Siepel, Cornell assistant professor of biological statistics and computational biology, Cornell postdoctoral researcher Brona Brejova and colleagues at several other institutions in the online version of the journal Genome Research, and it will appear in the December print edition. The complete human genome was sequenced several years ago, but that simply means that the order of the 3 billion or so chemical units, called bases, that make up the genetic code is known. What remains is the identification of the exact location of all the short sections that code for proteins or perform regulatory or other functions. More than 20,000 protein-coding genes have been identified, so the Cornell contribution, while significant, doesn't dramatically change the number of known genes. What's important, the researchers say, is that their discovery shows there still could be many more genes that have been missed using current biological methods. These methods are very effective at finding genes that are widely expressed but may miss those that are expressed only in certain tissues or at early stages of embryonic development, Siepel said. "What's exciting is using evolution to identify these genes," Siepel said. "Evolution has been doing this experiment for millions of years. The computer is our microscope to observe the results." Four different bases -- commonly referred to by the letters G, C, A and T -- make up DNA. Three bases in a row can code for an amino acid (the building blocks of proteins), and a string of these three-letter codes can be a gene, coding for a string of amino acids that a cell can make into a protein. Siepel and colleagues set out to find genes that have been "conserved" -- that are fundamental to all life and that have stayed the same, or nearly so, over millions of years of evolution. The researchers started with "alignments" discovered by other workers -- stretches up to several thousand bases long that are mostly alike across two or more species. Using large-scale computer clusters, including an 850-node cluster at the Cornell Center for Advanced Computing, the researchers ran three different algorithms, or computing designs -- one of which Siepel created -- to compare these alignments between human, mouse, rat and chicken in various combinations. Over millions of years, individual bases can be swapped -- C to G, T to A, for example -- by damage or miscopying. Changes that alter the structure of a protein can kill the organism or send it down a dead-end evolutionary path. But conserved genes contain only minor changes that leave the protein able to do its job. The computer looked for regions with those sorts of changes by creating a mathematical model of how the gene might have changed, then looking for matches to this model. After eliminating predictions that matched already known genes, the researchers tested the remainder in the laboratory, proving that many of the genes could in fact be found in samples of human tissue and could code for proteins. The researchers were sometimes able to identify the proteins by comparison with databases of known proteins. The discovered genes mainly have to do with motor activity, cell adhesion, connective tissue and central nervous system development, functions that might be expected to be common to many different creatures. The entire project, from building and testing the mathematical models to running final laboratory tests, took about three years, Siepel said. The work was supported by the National Cancer Institute, a National Science Foundation Early Career Development Grant and a University of California graduate research fellowship. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links Cornell University All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here
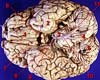 Washington DC (SPX) Nov 22, 2007
Washington DC (SPX) Nov 22, 2007Researchers have added a new piece to the puzzle of how the brain selectively amplifies those distinctions that matter most from the continuous cascade of sights, sounds, and other sensory input. Whether recognizing a glowering face among smiling ones or the unmistakable sound of a spouse calling one's name, such "categorical perception" is central to sensory function. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |