| . |  |
. |
Columbia, MO (SPX) Jun 10, 2008 At noon, it was black as night. It was May 19, 1780 and some people in New England thought judgment day was at hand. Accounts of that day, which became known as 'New England's Dark Day,' include mentions of midday meals by candlelight, night birds coming out to sing, flowers folding their petals,and strange behavior from animals. The mystery of this day has been solved by researchers at the University of Missouri who say evidence from tree rings reveals massive wildfires as the likely cause, one of several theories proposed after the event, but dismissed as 'simple and absurd.' "The patterns in tree rings tell a story," said Erin McMurry, research assistant in the MU College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources Tree Ring Laboratory. "We think of tree rings as ecological artifacts. We know how to date the rings and create a chronology, so we can tell when there has been a fire or a drought occurred and unlock the history the tree has been holding for years." Limited ability for long-distance communication prevented colonists from knowing the cause of the darkness. It was dark in Maine and along the southern coast of New England with the greatest intensity occurring in northeast Massachusetts, southern New Hampshire and southwest Maine. In the midst of the Revolutionary War, Gen. George Washington noted the dark day in his diary while he was in New Jersey. Nearly 230 years later, MU researchers combined written accounts and fire scar evidence to determine that the dark day was caused by massive wildfires burning in Canada. "A fire comes along and heat goes through the bark, killing the living tissue. A couple of years later, the bark falls off revealing the wood and an injury to the tree. When looking at the rings, you see charcoal formation on the outside and a resin formation on the top that creates a dark spot," said Richard Guyette, director of the Tree Ring Lab and research associate professor of forestry in the MU School of Natural Resources. The researchers studied tree rings from the Algonquin Highlands of southern Ontario and many other locations. They found that a major fire had burned in 1780 affecting atmospheric conditions hundred of miles away. Large smoke columns were created and carried into the upper atmosphere. "This study was a unique opportunity to take historical accounts and combine them with modern technology and the physical historical evidence from the tree rings and solve a mystery with science," McMurry said. The study - "Fire Scars Reveal Source of New England's 1780 Dark Day" - was published in the International Journal of Wildland Fire. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links University of Missouri-Columbia Forest and Wild Fires - News, Science and Technology
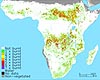 Leicester, UK (SPX) May 28, 2008
Leicester, UK (SPX) May 28, 2008A geographer from the University of Leicester has produced for the first time a map of the scorched Earth for every year since the turn of the Millennium. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |