| . |  |
. |
St Louis MO (SPX) Feb 10, 2006 A new, more robust analysis of recently derived human gene trees by Alan R. Templeton, Ph.D, of Washington University in St Louis, shows three distinct major waves of human migration out of Africa instead of just two, and statistically refutes � strongly � the 'Out of Africa' replacement theory. That theory holds that populations of Homo sapiens left Africa 100,000 years ago and wiped out existing populations of humans. Templeton has shown that the African populations interbred with the Eurasian populations � thus, making love, not war. "The 'Out of Africa' replacement theory has always been a big controversy," Templeton said. "I set up a null hypothesis and the program rejected that hypothesis using the new data with a probability level of 10 to the minus 17th. In science, you don't get any more conclusive than that. It says that the hypothesis of no interbreeding is so grossly incompatible with the data, that you can reject it." Templeton's analysis is considered to be the only definitive statistical test to refute the theory, dominant in human evolution science for more than two decades. "Not only does the new analysis reject the theory, it demolishes it," Templeton said. Templeton published his results in the Yearbook of Physical Anthropology, 2005. A trellis, not a tree He used a computer program called GEODIS, which he created in 1995 and later modified with the help of David Posada, Ph.D., and Keith Crandall, Ph.D. at Brigham Young University, to determine genetic relationships among and within populations based on an examination of specific haplotypes, clusters of genes that are inherited as a unit. In 2002, Templeton analyzed ten different haplotype trees and performed phylogeographic analyses that reconstructed the history of the species through space and time. Three years later, he had 25 regions to analyze and the data provided molecular evidence of a third migration, this one the oldest, back to 1.9 million years ago. "This time frame corresponds extremely well with the fossil record, which shows Homo erectus expanding out of Africa then," Templeton said. Another novel find is that populations of Homo erectus in Eurasia had recurrent genetic interchange with African populations 1.5 million years ago, much earlier than previously thought, and that these populations persisted instead of going extinct, which some human evolution researchers thought had occurred. The new data confirm an expansion out of Africa to 700,000 years ago that was detected in the 2002 analysis. "Both (the 1.9 million and 700,000 year) expansions coincide with recent paleoclimatic data that indicate periods of very high rainfall in eastern Africa, making what is now the Sahara Desert a savannah," Templeton said. "That makes the timing very amenable for movements of large populations through the area." Templeton said that the fossil record indicates a significant change in brain size for modern humans at 700,000 years ago as well as the adaptation and expansion of a new stone tool culture first found in Africa and later at 700,000 years expanded throughout Eurasia. "By the time you're done with this phase you can be 99 percent confident that there was recurrent genetic interchange between African and Eurasian populations," he said. "So the idea of pure, distinct races in humans does not exist. We humans don't have a tree relationship, rather a trellis. We're intertwined." Related Links Washington University 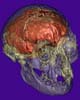 Hanover NH (SPX) Feb 06, 2006
Hanover NH (SPX) Feb 06, 2006Two Dartmouth researchers are one step closer to defining exactly when human maturity sets in. In a study aimed at identifying how and when a person's brain reaches adulthood, the scientists have learned that, anatomically, significant changes in brain structure continue after age 18. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |