| . |  |
. |
Delft, Netherlands (SPX) May 28, 2008 For the first time, researchers at Delft University of Technology have witnessed the spontaneous repair of damage to DNA molecules in real time. They observed this at the level of a single DNA molecule. Insight into this type of repair mechanism is essential as errors in this process can lead to the development of cancerous cells. Researchers from the Kavli Institute of Nanoscience Delft are to publish an article on this in the leading scientific journal Molecular Cell. Cells have mechanisms for repairing the continuous accidental damage occurring in DNA. These damages can vary from a change to a single part of the DNA to a total break in the DNA structure. These breaks can, for instance, be caused by ultraviolet light or X-rays, but also occur during cell division, when DNA molecules split and form two new DNA molecules. If this type of break is not properly repaired it can be highly dangerous to the functioning of the cell and lead to the creation of a cancerous cell. One major DNA-repair mechanism involved in repairing these breaks is known as homologous recombination. This mechanism has been observed for the first time by Delft University of Technology researchers in real time and at the level of a single DNA molecule. To observe this, a DNA molecule is stretched between a magnetic bead and a glass surface. A force is exerted on the magnetic bead using a magnetic field, enabling researchers to pull and rotate a single DNA molecule in a controlled fashion. As the position of the bead changes when the DNA molecule is repaired, researchers are able to observe the repair process in detail. Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Delft University of Technology Darwin Today At TerraDaily.com
 Boston MA (SPX) May 28, 2008
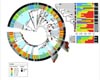
Boston MA (SPX) May 28, 2008Marine bacteria in the wild organize into professions or lifestyle groups that partition many resources rather than competing for them, so that microbes with one lifestyle, such as free-floating cells, flourish in proximity with closely related microbes that may spend life attached to zooplankton or algae. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |