| . |  |
. |
Bristol, UK (SPX) Jul 10, 2008 The speed at which we react to threatening situations can have life or death implications. In the more primitive past, it could have meant escaping a wild animal; today it might mean swerving to avoid a head-on car crash. It has been thought for some years that mammals have two decision-making systems in their brains which operate at different speeds to cope with different situations. New research from the University of Bristol supports this theory and has shown that the evolutionary pressures arising from the older, faster, but less accurate, part of the brain may have shaped the more recent development of the slower-acting but more precise cortex, found in humans and higher animals. The research has been published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B. Pete Trimmer, lead author on the study, explained: "If we compare the brain of a human with that of a reptile, we find they are very similar except that mammals have a large 'outer cortex' around the outside of the existing 'sub-cortical' brain, that is common to other vertebrates. "The fact that lizards make decisions indicates that the sub-cortical brain in humans is also likely to be used in decision-making. However, fMRI scans now reveal that parts of the outer cortex (which developed more recently in our evolutionary past) are also used when making decisions." Why does the brain need these two decision-making areas? What benefit does the new cortex bring? After all, extra brain means extra weight and energy required to carry it around. Furthermore, is the older sub-cortical system now largely redundant? If so, could we expect it to atrophy in future humans so our brains become smaller? To address these questions, Trimmer built theoretical models representing the two systems in which the sub-cortical system was assumed to act very quickly but inaccurately, whereas the cortex allowed information to be gathered before making an informed decision, and was therefore slower. The results of their modelling showed that when the threat level is high, such as the risk of being attacked by a dangerous animal, it is very useful to have the fast-acting, if inaccurate, system. But when dealing with situations which don't occur very often, or complex scenarios with many conflicting cues such as social situations, the cortical system is of more use than the sub-cortical system. Trimmer commented: "As life became more complex, the benefit of gathering information before making a decision put an evolutionary pressure on the early brain. This may have led to the rapid development of the cortex in mammals. So if humans continue to live in a world of dangers such as wild animals or fast-moving cars, there will still be an evolutionary benefit to maintaining the sub-cortical system, and it is unlikely to atrophy in future humans."
Community
Related Links University of Bristol All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here
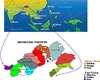 Washington DC (SPX) Jul 07, 2008
Washington DC (SPX) Jul 07, 2008North-east India has always been a hotspot for population geneticists due to its unique, strategic geographic location and the presence of linguistically, culturally and demographically diverse populations practicing varied occupations (from hunter-gathering to settled agriculture). |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |